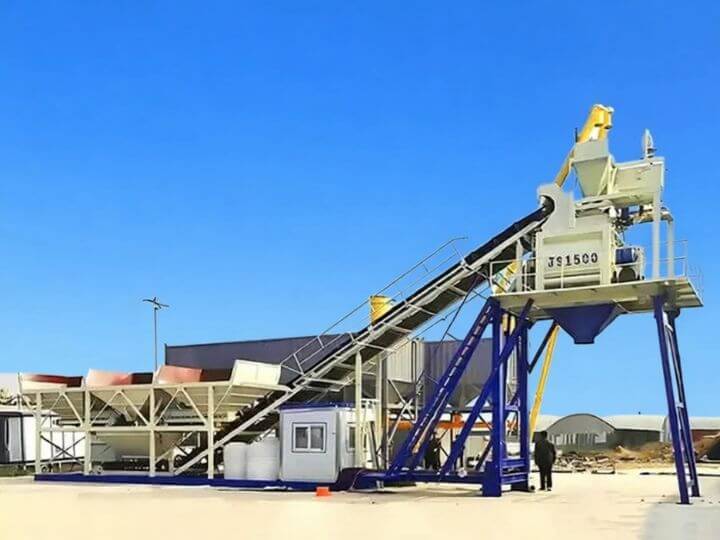
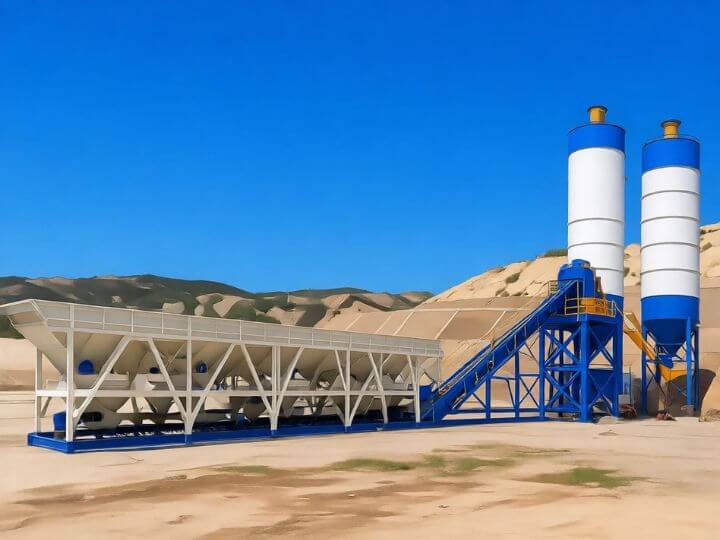
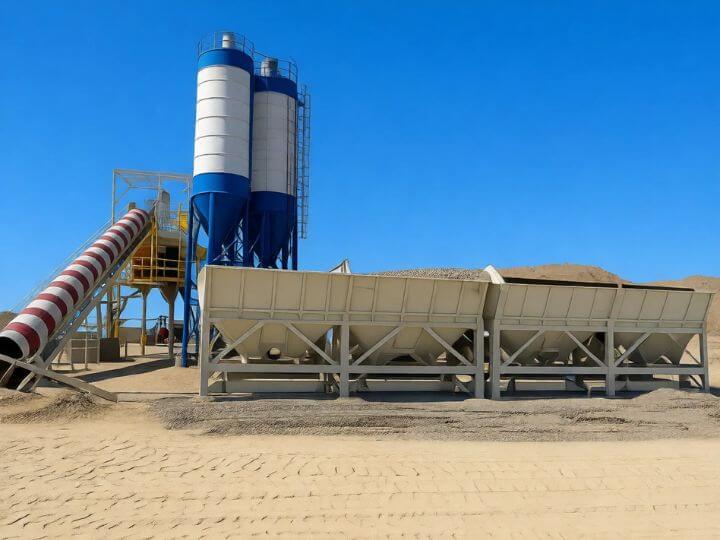
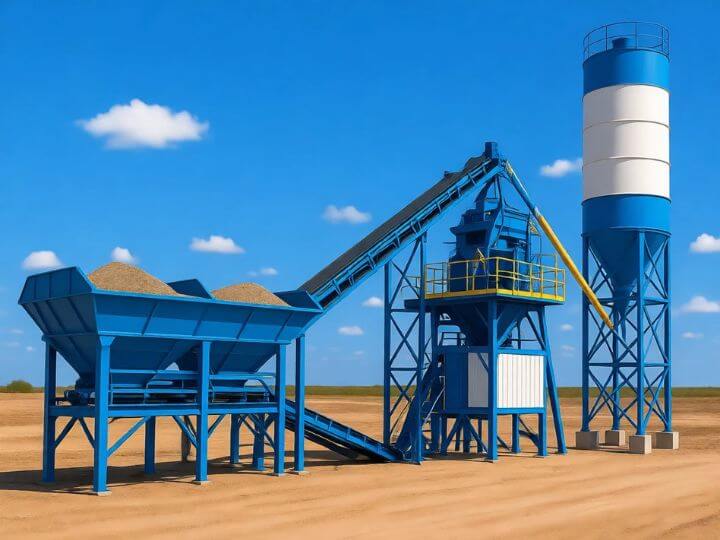
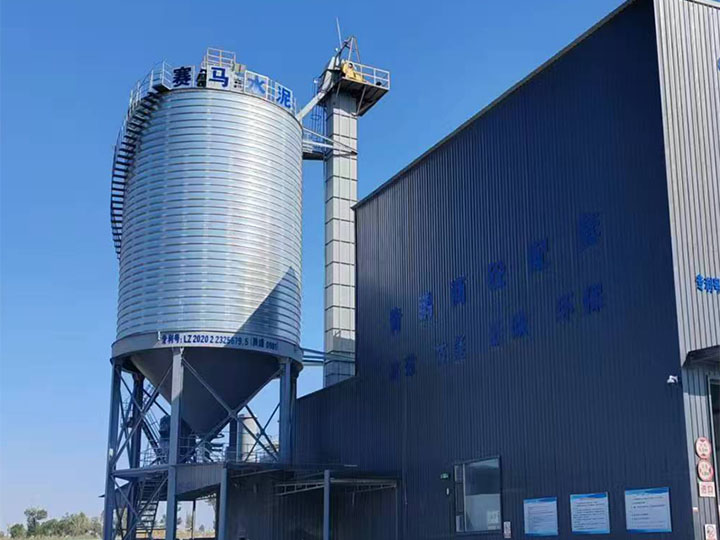
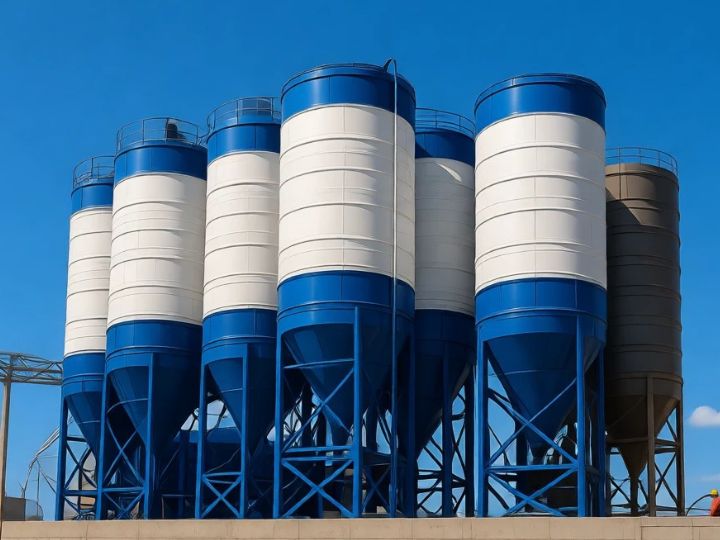
Shanghe Concrete Batching Plant
A concrete batching plant that combines aggregates, cement, water, and additives in exact proportions to manufacture consistent, high-grade concrete for construction applications. The foundation-free concrete batching plant is available in a comprehensive range of capacities to meet every project demand, including models MHZS60, MHZS90, MHZS120, and MHZS180 from 60m³/h and 90m³/h, up to 120m³/h and 180m³/h.
This foundation-free concrete batching plant eliminates the need for permanent foundations, enabling rapid deployment and easy relocation. Perfect for temporary projects or sites requiring frequent moves, it delivers reliable performance, high output, and straightforward operation—all while significantly reducing installation time and costs. Foundation-free concrete plants are a suitable solution for a wide range of projects, including road and bridge construction, rural infrastructure development, and emergency repair works.
The fundamental difference is in mobility versus permanence. A traditional plant is a fixed installation requiring deep, reinforced concrete foundations and significant civil works. A foundation-free plant replaces this with its own rigid steel platform, needing only a level, compacted surface for setup. This eliminates weeks of preparatory work, drastically reducing both cost and installation time.
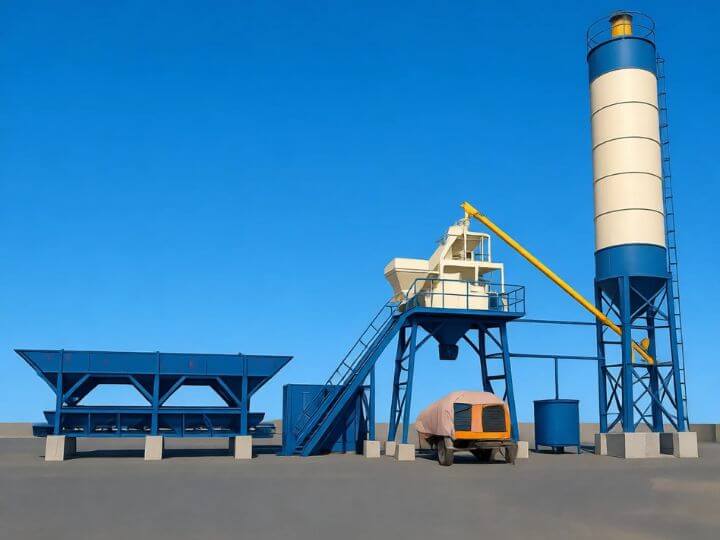

Advantages
Operational & Economic Advantages:
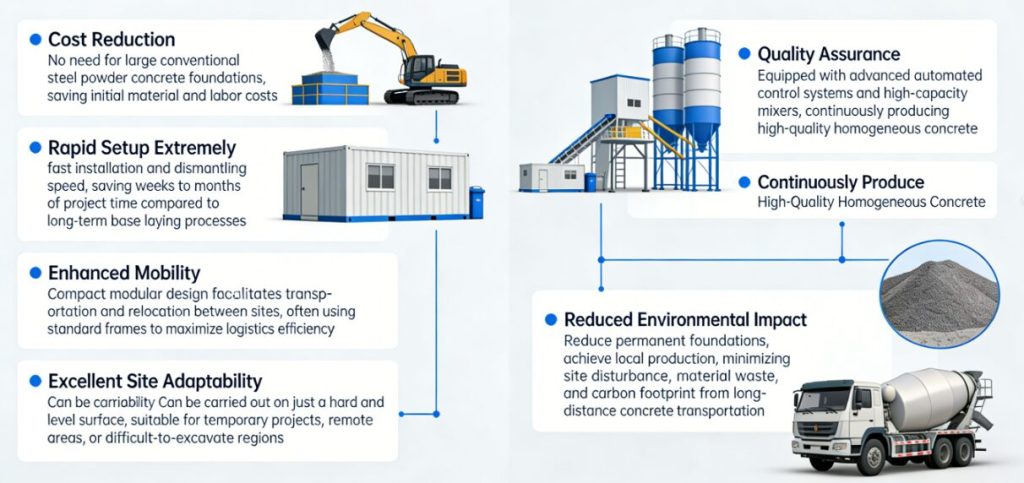
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating the need for large, permanent reinforced concrete foundations, they save substantially on upfront material and labor expenses.
- Rapid Deployment: Installation and dismantling are exponentially faster, saving weeks or even months of project time by removing the lengthy foundation-laying process.
- Enhanced Mobility: Their compact, modular design is built for easy transport and relocation between sites, often using standard shipping containers for maximum logistics efficiency.
- Superior Site Adaptability: They require only a hard, level surface to operate, making them ideal for temporary projects, remote locations, or areas where excavation is difficult.
Performance & Sustainability Benefits:
- Guaranteed Quality: Equipped with advanced automated control systems and high-performance mixers, they consistently produce a uniform, high-grade concrete mix.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimizing permanent foundations and enabling local production cuts down on site disruption, material waste, and the carbon footprint associated with long-distance concrete transport.
Working Principle
Operation is governed by an automated control system that manages the precise batching and mixing of materials according to specific mix designs. The workflow follows these key stages:
- Material Storage & Feeding: Raw materials are stored in dedicated compartments: aggregates (sand, gravel) in bins, cement in sealed silos, and water/admixtures in tanks.
- Precise Weighing (Batching): The control system automatically dispenses each material into high-precision weigh hoppers. Flow stops exactly when the programmed weight is reached, ensuring mix accuracy and consistency.
- Conveying to Mixer: Weighed materials are transferred to the central mixer:
- Aggregates move via belt conveyor or hopper.
- Cement is transported through sealed screw conveyors.
- Water and admixtures are pumped through pipelines.
- Mixing: Materials are combined in a compulsory mixer (typically a twin-shaft type). Rotating blades forcefully blend the mix for a set time (60–120 seconds) to achieve complete uniformity.
- Discharge & Transport: The fresh concrete is discharged directly into a waiting transit mixer truck for delivery to the site.
Components
Primary Structural & Mobility Components
- Integrated Steel-Frame Chassis/Platform: This is the core of the foundation-free design. It is a robust, welded steel structure that unifies all major components (mixer, aggregate bins, conveyor, cement silo base) into a single, transportable unit. It distributes operational loads and requires only a flat, compacted surface for placement.
- Modular Panels & Walkways: The plant is clad with easily bolted-on steel or aluminum panels, guardrails, and stairways. This modularity allows for rapid assembly and disassembly while ensuring safety and weather protection.
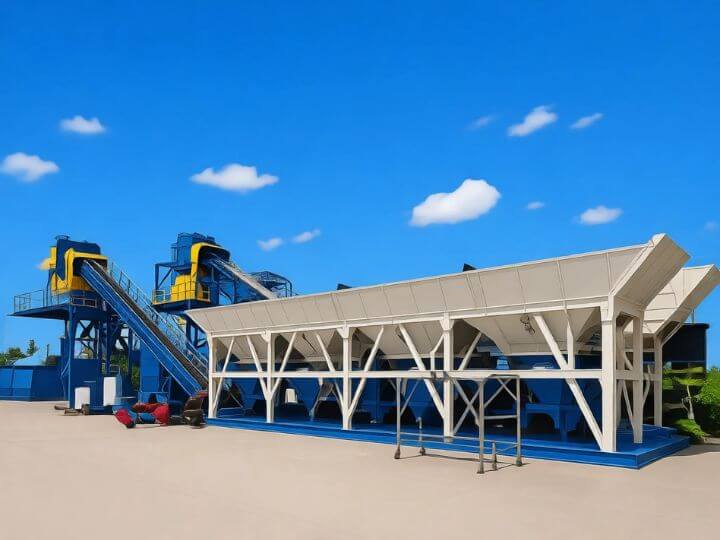

Core Material Handling Components
- Aggregate Storage & Feeding System:
- Aggregate Bins: Multiple compartments (typically 2-4) for storing different sizes of sand, gravel, or crushed stone. They are mounted directly onto the main chassis.
- Aggregate Feeder: Located under each bin, often using belt feeders or vibratory feeders to ensure a consistent and controlled flow of material onto the conveyor.
- Aggregate Conveyor: An inclined belt conveyor (or sometimes a bucket hoist) that transports the aggregates from the feeder to the top of the plant for weighing and mixing.
- Cement Storage & Conveying System:
- Cement Silos: One or more vertical, cylindrical steel silos for storing cement, fly ash, or other powders. For mobility, these are separate, free-standing units placed next to the main plant but designed for easy disconnection and transport.
- Screw Conveyor: A sealed, rotating screw mechanism that pneumatically or mechanically transfers cement from the silo to the cement weigh hopper on the main plant.
- Liquid Storage System:
- Water Tank: A tank, often integrated into the chassis frame, that stores mixing water.
- Admixture Tanks: Smaller tanks for storing liquid chemical admixtures (plasticizers, accelerators, etc.).
- Pumps & Piping: A network of pumps and pipes to deliver water and admixtures to their respective weigh scales or directly to the mixer.
Batching, Mixing & Control Components
- Weighing System (The Batcher): The heart of precision. This consists of several suspended weigh hoppers or load cells:
- Aggregate Weigh Hopper: Located at the top of the conveyor discharge, it receives and precisely weighs the aggregates.
- Cement Weigh Hopper: Weighs the cement from the screw conveyor.
- Water & Admixture Weigh Scale: Typically a weighing tank that accurately measures liquids before injection.
- Mixer Unit:
- Compulsory Mixer: Usually a high-efficiency twin-shaft paddle mixer mounted centrally on the chassis. It ensures fast, homogeneous mixing of all ingredients. The mixer’s discharge chute is positioned to load transit mixer trucks below.
- Control System:
- Central Control Panel/Computer: An automated, often computerized system that stores mix designs, controls the entire batching sequence, manages material flow, records production data, and ensures consistent quality. It is housed in a protective cabin on the plant.
Auxiliary & Supporting Components
- Dust Collection System: A network of filters (bag filters) and piping connected to cement transfer points (silo top, mixer inlet) to capture airborne powder, ensuring environmental compliance and a clean operation.
- Air Compressor: Provides pneumatic power for operating valves, cement discharge gates, and the dust collection system.
- Electrical Power Pack: A centralized cabinet housing all electrical components, motors, and drives. It is designed for quick connection to a site power source or generator.
- Hydraulic System (if applicable): Some plants use hydraulics to operate aggregate bin gates, mixer discharge gates, and other moving parts.
Specification
| Model | MHZS60 | MHZS90 | MHZS120 | MHZS180 |
| Production capacity (m3/h) | 60m³ | 90m³ | 120m³ | 180m³ |
| Concrete mixer | JS1000 | JS1500 | JS2000 | JS300 |
| Total Installed Capacity(kw) | 100 | 165 | 210 | 260 |
| Cycle period | 60S | 60S | 60S | 30S |
| Cement/Powder Silo Capacity(set) | 3×100T | 3×100T | 4×100T or 200T | 4×200T |
| Largest aggregate particle | Φ80mm | Φ80mm | Φ120mm | Φ120mm |
| Batching station | PLD1600 | PLD2400 | PLD3200 | PLD4800 |
| Standard Discharging Height(m) | 4.2m | 4.2m | 3.8~4.5 | 4.5 |







